It is no secret that websites are vulnerable to hackers, bots and malware. Nowadays, it is even more important to make sure our websites are secure from cyber-attacks as hackers have become more sophisticated in their methods.
WordPress has become the most popular platform for blogging and website building, so it is essential to know the best practices to secure your WordPress website in 2023.
Whether you are just starting out or have been running a WordPress site for some time, staying ahead of the game is crucial to your website’s safety and success.
In this blog post, you will find out best practices to lock down your WordPress website, tips on choosing the right hosting service and more.
We will discuss how to ensure you are using the latest version of WordPress, how firewall security can protect against malicious attacks and much more.
We will also look into the importance of backing up your WordPress site, so you can restore it should anything go wrong. With these must-know practices, you can rest assured that your WordPress website is as secure as possible for this 2023.
20 WordPress Security Best Practices
1. Choose Secure Hosting for WordPress
The first step in keeping your WordPress site secure is choosing a hosting provider. You want a hosting provider that has a solid reputation for security and that is up-to-date. You should steer clear of shared hosts. You want to be on a virtual private server (VPS) or a dedicated server, which usually costs around $10-$12 per month or half if you know how to manage cloud VPS on a shell access.
I personally used Vultr and Digital Ocean on my personal and client websites paired with BunnyShell and ServerAvatar to manage my VPS with ease. Popular similar setups include Cloudways, GridPane, WPEngine and many more.
Many hosts offer WordPress-optimized hosting to meet the specific needs of a WordPress website. If you’re unsure, ask your host what they offer. There are also several WordPress-specific hosting providers that are designed to keep your site safe.
2. Install an SSL Certificate

The second step is to install a Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) certificate on your WordPress website. This will encrypt the data that is transmitted between your visitors’ browsers and your website. The encryption makes it much harder for hackers to access your data.
Most web hosting supports Free Let’s Encrypt SSL, but others do not support this. There are other alternatives that you can use. Some free SSL providers give you 3-months access and you need to set it up again.
For paid SSL, the average costs for this is around $12-$80/year or more, depending on that type of SSL certificates you need for your website.
What are HTTPS and SSL?
HTTPS is a more secure version of HTTP and is used in combination with SSL certificates. SSL certificates use a public-private key encryption to establish a secure connection between the server and the browser. With SSL certificates enabled, your browser will display a padlock icon in the address bar, indicating that your connection is encrypted.
Why you need to use HTTPS
The HTTPS and SSL protocols are used to encrypt data sent between a web server and a browser, thus preventing the data from being intercepted and read.
3. Back-Up Your Website
Webmasters typically have their own methods for creating back-ups and often use a combination of several methods to ensure that the back-ups are current and accessible, including:
- Local Host backup or Server backup
- Database back-up
- Full website backup
- Incremental backups
- Scheduled remote backups
- Staging/Development Clones of the Production website
The importance of a database back-up is that it keeps an exact copy of the database that is being used by the website and can be used to quickly restore the website in case the most recent files and the database are lost.
Check out the best WordPress backup plugins available in the market today.

Bloggers who use WordPress should make database backups a part of their weekly maintenance routine. If you follow these best practices, you’ll be able to handle the worst case scenarios with ease. My recommended backup plugin for WordPress is WPVivid Pro which supports all the features mentioned above.
Other popular backup plugins include BlogVault, Updraft Plus, BackupBuddy, WP Time Capsule, and many more.
4. Keep Your Plugins and Theme Up to Date
The best way to keep your site secure is to keep everything up-to-date. This includes all of your plugins and themes as well as your core WordPress installation.
It is a good practice, before you update all your themes and plugins, is to backup your website first, as there are times that a major plugin update can cause conflict to other plugins leading to a WordPress fatal error.
Many websites are still running older versions of WordPress, and that’s a huge security risk. The best way to avoid this is to keep everything updated regularly.
Remove Unused WordPress Plugins and Themes
To prevent having a bunch of outdated plugins, simply uninstall the ones that you are not using. This will also help save space on your server resources such as storage space and bandwidth.
Do Not Install Nulled Plugins and Themes
If you have hired an agency or web developer to create your website, be sure to check with them if the plugins they have installed are free version or paid with dedicated licenses, not Nulled because these are vulnerable to potential threats or attacks.
You can also have it checked with other WordPress developers to make sure that all plugins and themes installed are not Nulled versions.
5. Install WordPress Security Plugins
Using a good security plugin, you can protect your website from hackers, brute force and other attacks. WordPress security plugins are a great way to keep your website secure.
Popular security plugins for WordPress include:
- Malcare (check out my unbiased review of Malcare Security)
- WordFence
- Astra Security
- Patch Stack
- Sucuri.
- iThemes Security
- Hide My WP Ghost – Security Plugin
With any of the tools above, you can conduct regular WordPress security scans to ensure your website is malware-free and protected from potential threats.
Malcare WordPress security plugin for example can also remove malware if your website was hacked or infected by a malware by just a single click. No need to hire a developer to do it, as the plugin itself will pinpoint the exact infected files and will generate a troubleshooting report once fixed.
6. Update to the latest version of PHP
There is an ongoing debate about the most secure version of PHP. The biggest difference between the supported versions is the fact that older versions do not support newer features. Because of this, it is time to update your site to the latest version of PHP. This will ensure that you are using the latest security features in PHP and that your site is compatible with the latest WordPress versions.
If you’re running a self-hosted WordPress website, upgrading to the latest version of PHP is a must. The trouble is, many webmasters don’t update as often as they should because they don’t know how to, or they don’t know what the latest versions of PHP actually do.
Each version of PHP has a different set of features, so it’s important to stay up-to-date to get the most out of WordPress and your web hosting provider. The latest version of PHP is 8.2, and the previous versions of PHP that you should update to, if you haven’t already, are 5.3.3, 5.4.45, 5.5.38, 5.6.29, 7.2, 8.0, and 8.1.
7. Create a Strong Login Combination

It’s not so easy to hack WordPress. But using an old and weak password is an open door for every intruder.
A strong login combination should be taken into account to protect the WordPress blog from unauthorized access. The stronger the login password the stronger the protection. It is not very hard to set up a strong login combination for your WordPress account.
Anyone with an average knowledge of computers can do it.
It is also good practice to change the default “admin” username and the default WP login URL to minimize the brute force attacks to your website.
8. Change Default WordPress Login URL
The default WordPress login URL is http://example.com/wp-admin/ . This is a security risk because hackers can easily guess this URL and attempt to guess the administrator’s login name and password. To avoid the risk of the default login URL being guessed, change the URL to something unique to your site which can be done by the help of other plugins and custom coding.
9. Disable File Editing in the WordPress dashboard
One of the biggest mistakes you can make when managing a WordPress site is to enable users to edit files directly in the WordPress dashboard. The WordPress dashboard is a great way to manage your site, but it’s also the perfect place for hackers to attack.
If hackers gain access to the dashboard, they could easily edit your PHP files and insert malicious code into your site. You can easily avoid these attacks by disabling file editing in the WordPress dashboard. If you want to allow people to edit files in the dashboard, there are plugins that allow you to restrict which files can be edited.
10. Stay on top of Spam

There are two main ways to prevent spam which are the following.
Using Captcha – This is a simple test that is used to stop robots from registering your website and using it to send spam. Captcha works by asking the user to select a word that is shown on the screen. This is a great way to stop people from using a computer to register your site and send spam.
Popular captcha service is Recaptcha by Google. There’s also alternative such as Hcaptcha.
Using Honeypot – A honeypot is another method of stopping spam. The honeypot works by luring the spammer into thinking that they are entering all of the information necessary to register your website, but in reality all of the information entered is fake. This will hopefully prevent them from sending spam to your website.
Popular honeypot that I tested is WP Armour. This is the plugin I used to stop email spams that even Recaptcha by Google can’t block.
11. Install Activity Log
The activity log has been around since WordPress 2.7, and it’s a useful tool for most users. The activity log records the changes that you make to your WordPress site, such as posts and pages that you create, changes you make to your theme or plugins, and track a culprit if a security breach happens. This easy to use plugin will be a perfect solution to your problem.
12. Limit Login Attempts
The WordPress login is the most common place for a hacker to attack your website. They will attempt to brute force the password and try to log in with the wrong password. This is why the WordPress login page has the option to limit login attempts to prevent from unexpected entry.
13. Limit WordPress User Permissions
Restricting access to your WordPress admin is a must when it comes to keeping your WordPress website secure. Too many times we have seen people giving out their WordPress login to other people so they can manage their website for them. We recommend that you never give out your WordPress login to anyone.
If you want to give someone the right to manage your website, create a new user account for them. And don’t forget to give them any login credentials they need to access your website.
13. Disable xmlrpc.php File
The xmlrpc.php file is a core file and is required by WordPress to run. It handles the XML-RPC requests from any other website or application that makes use of your WordPress site. Unfortunately, it also allows anyone to access your site from the Internet and to install WordPress on it.
This feature can be very useful for a developer who wants to install WordPress on localhost for testing, but it is a big security risk for a live website. Limit the use of xmlrpc.php : If you are not using the WordPress XML-RPC functionality, you can disable the file by simply installing this plugin called Disable XML-RPC-API By Neatma.
14. Block Hotlinking to Prevent Server Crash
Hotlinking is a popular method for delivering the same content to multiple websites without the need to download the file from the original site. It’s a legitimate thing to do, but it can be a big problem for webmasters who work hard to maintain a fast website.
If you have a WordPress blog, you may be familiar with hot linking, as it’s often used as a way to share images to other blogs and websites. The problem is, it can put a lot of strain on the web hosting or server hosting the original content of the website. As a result, the server may slow down or even crash.
In fact, hotlinking is one of the most common causes of server overload. Most web hosting comes with Hotlink protection that you can easily activate. There are also WordPress plugins that can enable this, such as AIO WP Security.
15. Manage File Permissions
File and directory permissions are a basic security measure to protect your website from unauthorized access. If a user has permission set to 777, this means they can access, view and edit files and directories.
This is a common mistake that WordPress developers make, and can be easily prevented by setting the permissions on your directories and files properly.
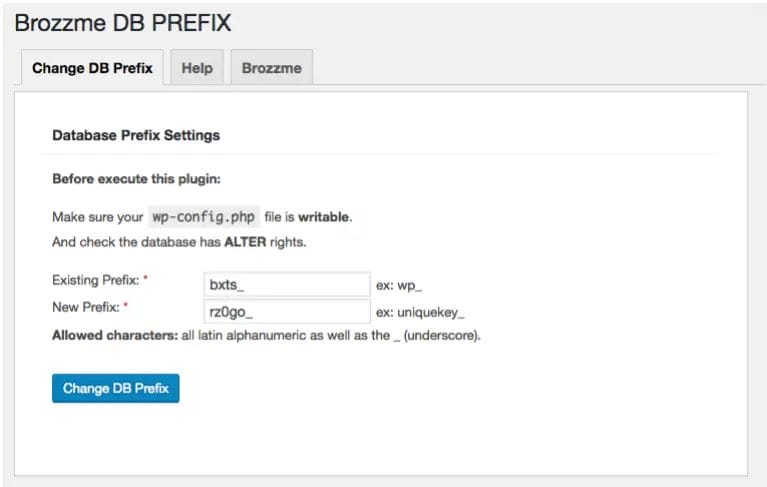
16. Change WordPress Database Prefix
One of the most important steps you can take to protect your site is changing the default WordPress database prefix. WordPress database prefix is a string that is used in the wp-config.php file to define the name of your MySQL database. By default, WordPress uses the name “wp_” but it is quite easy to change it to something else. If you do change it to something else, it will make it harder to hack your WordPress website.
To change this, go to your hosting file manager and locate the file wp-config.php and look for the code with $table_prefix = ‘wp_’; and replace it with something else; in this case, we replaced it with ‘tpdbase_’:
Next step you need to do is go to PhpMyAdmin and replace all instances of wp_ to tpdbase_ on the SQL table.
Another easy fix is by installing this plugin called Brozzme DB Prefix & Tools Addons By Benoti.
17. Add Two Factor Authentication

Using a strong password is great, but it’s not enough to secure your WordPress account. You should also consider using a two-factor authentication solution. A two-factor authentication is an additional layer of security that protects your account even if your password is compromised. It’s easy to set up, and it only takes a minute of your time to do so.
18. Hide WP and Plugin Versions
The version of your WordPress site can tell a lot more than you realize. Updates that WordPress releases list all of the changes and bug fixes made, so hackers know which ones are vulnerable. That’s why it’s so important to hide your WordPress version number. It’s easy for a hacker to find by just viewing the source code. To prevent this, you should always update your WordPress version, either when prompted or even automatically. If your update is overlooked, it’s better to take extra steps and hide your version number.
One of the best solution for this is by using this plugin called Hide My WP Ghost – Security Plugin. It does a lot of things including hiding the versions of your plugins, themes and WordPress.

19. Automatically Force Log Out Idle Users
One of the easiest ways to secure your website is to automatically send users who have been inactive for a set period of time to a logout page. This is especially important if your website is public facing.
One of the easiest and fastest solution for this is using a plugin called Inactive Logout By Deepen Bajracharya
The Inactive Logout plugin is an easy and effective way to keep your WordPress site secure. It works by detecting when users have been inactive and automatically logging them out after a set period of time.
You can customize the timeout period in the plugin settings and even add a custom message informing the user their session is about to expire. This helps protect your site from unauthorized access and ensures users don’t forget to log out.The plugin is very easy to configure and use.
Once you install and activate the plugin simply configure the idle timeout from the plugin settings. So now any unattended idle WordPress user sessions will be terminated automatically.
You can also display a custom message to idle user sessions, alerting them that the session is about to end.
20. Check Open Ports on Server
The emergence of the Internet has led to the spread of any cyber attacks. The most common attack to a WordPress website is an open port at the server level. This is why it is important to have a secure hosting environment to protect your website from any kind of attacks.
These are the most common ports that needs to be open for your WordPress website. If you need specific port, be sure to contact your service provider to double check with them.
21 – default FTP port.
80 – default HTTP port.
110 – default POP3 port.
143 – default IMAP port.
443 – default SSL port.
587 – secure SMTP port.
993 – IMAP port over TLS/SSL.
995 – POP3 port over TLS/SSL.
3306 – default MySQL port.
22 – default SFTP port.
Why You Need WordPress Security
WordPress is a powerful platform for building websites and blogs, but it’s not immune to security vulnerabilities. Without proper security measures in place, your WordPress site can be exposed to malicious attacks that can compromise your website’s integrity and reputation. Investing in WordPress security is the best way to protect your site from cybercrooks and ensure that your data remains safe and secure.
How Safe is WordPress?
No platform is 100% secure, and WordPress is no exception. The platform’s popularity also makes it a target for hackers. If you want to be sure that your site is safe, then you need to follow as many as you can on the best practices mentioned above.
If you follow them, you’ll be able to avoid some of the most common issues that might come up.
mention stats / research
What are the common WordPress Security Issues?
Brute-Force Login Attempts
Brute-force attacks are one of the most common WordPress security issues. It’s an attempt to gain access to a website or a web application by sending large numbers of login attempts with commonly used usernames and passwords. The success rate of brute-force attacks is very low, in most cases less than 1%. However, they can be very annoying, especially when they target the login page. And they can consume a lot of resources on the server, which may cause it to become slow or even unresponsive.
Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
XSS (Cross-site scripting) is an attack, which allows an attacker to inject malicious scripts into your WordPress website. XSS attacks are executed by entering an attacker’s maliciously crafted code into a form field, or by uploading and executing a malicious file. WordPress by default has XSS protection and sanitization, but sometimes it can be bypassed by using some uncommon characters. That is why it is very important to always keep your WordPress and plugins updated and to always check your site for any malicious code.
Database Injections
A SQLI is an attack that attempts to inject malicious SQL code into an application’s database. This can allow a hacker to penetrate the application and execute commands that give them full control over the database.
Backdoors
Backdoors are malicious programs, scripts or commands that are embedded in your site. Backdoors are also known as web shells or rootkits. Backdoors are usually used by hackers to access your site (and server) from a remote location.
When a backdoor is present on a site, it allows the hacker to execute arbitrary code on the site, upload and download files, and potentially even grant access to the site to other unauthorized users.
Backdoors can be inserted into a website by exploiting vulnerabilities in outdated WordPress plugins or themes.
Denial-of-Service (DoS) Attacks
Denial-of-service (DoS) attacks are one of the most common attacks on uptime and website security. They are used by hackers to bring down websites and web servers. The goal of a denial-of-service attack is to overload the server and cause it to crash.
Phishing
Phishing is one of the most common problems found in WordPress websites, because they are easy to hack by even a beginner. Phishing occurs when a site tries to trick you into revealing your sensitive data, like credit card numbers, social security number, etc. Phishing is a very common problem in WordPress websites because most of the WordPress users are not aware of the security issues.
Hotlinking
The issue of hotlinking is one that plagues the internet, and blogs and websites are no exception. Hotlinking occurs when someone else uses your image as a link to their image, thereby saving bandwidth and server space on their end. Hotlinking is a problem because it costs you money in bandwidth and server space.
Outdated WordPress Plugins
If you run a WordPress site, you need to keep your plugins updated. Otherwise, when a security issue is found in a plugin, you’re putting your site at risk.
Outdated WordPress version
WordPress version is the main cause of WordPress Security Issues. WordPress releases new versions to fix security related issues. Updating WordPress to the latest version is the best way to prevent WordPress security issues.